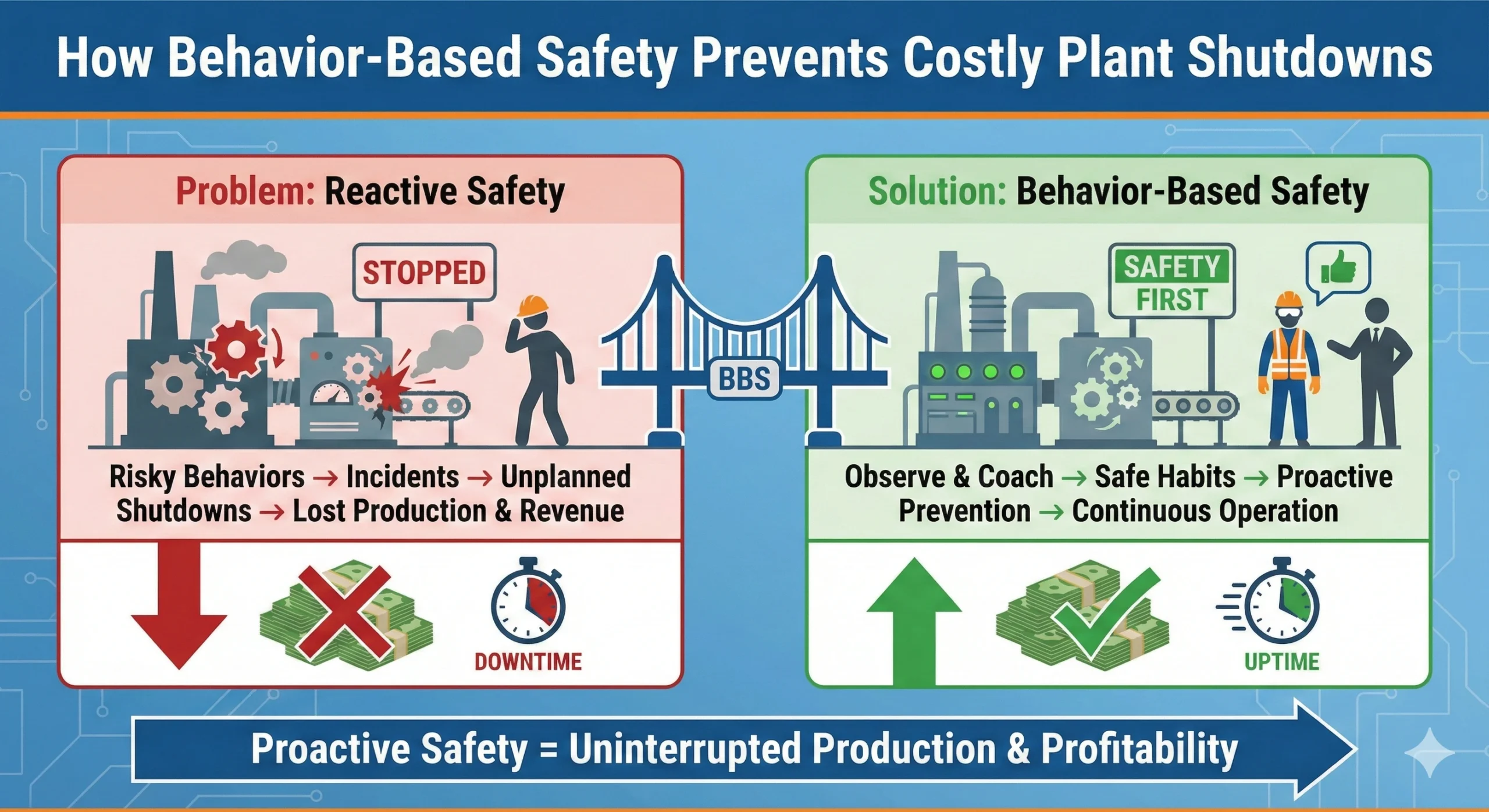
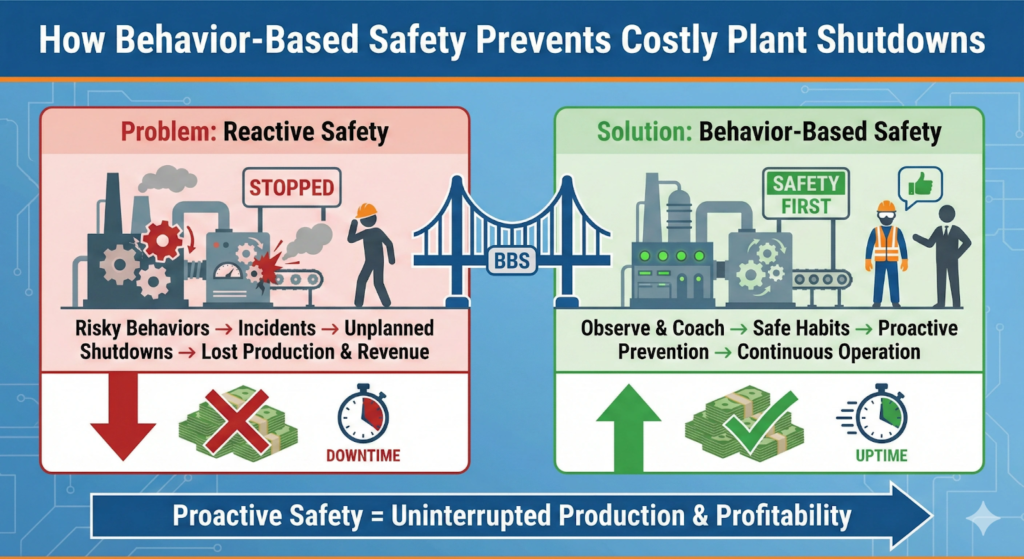
Behavior-based safety helps industrial plants prevent unplanned shutdowns by reducing human error, strengthening safety culture, and addressing risk before incidents disrupt operations.
What Behavior-Based Safety Is?
Observation-Based Risk Identification
Behavior-based safety (BBS) is a systematic approach that focuses on identifying unsafe and safe behaviors through structured observations. These observations reveal patterns that contribute to incidents before equipment or processes fail.
Employee-Centered Safety Systems
BBS places employees at the center of safety improvement by involving frontline workers in observing, reporting, and correcting behaviors. This shared responsibility strengthens engagement and accountability.
Continuous Improvement Framework
Rather than one-time training, BBS operates as an ongoing cycle of observation, feedback, and improvement. This allows safety practices to evolve alongside operational changes.
Why Plant Shutdowns Occur
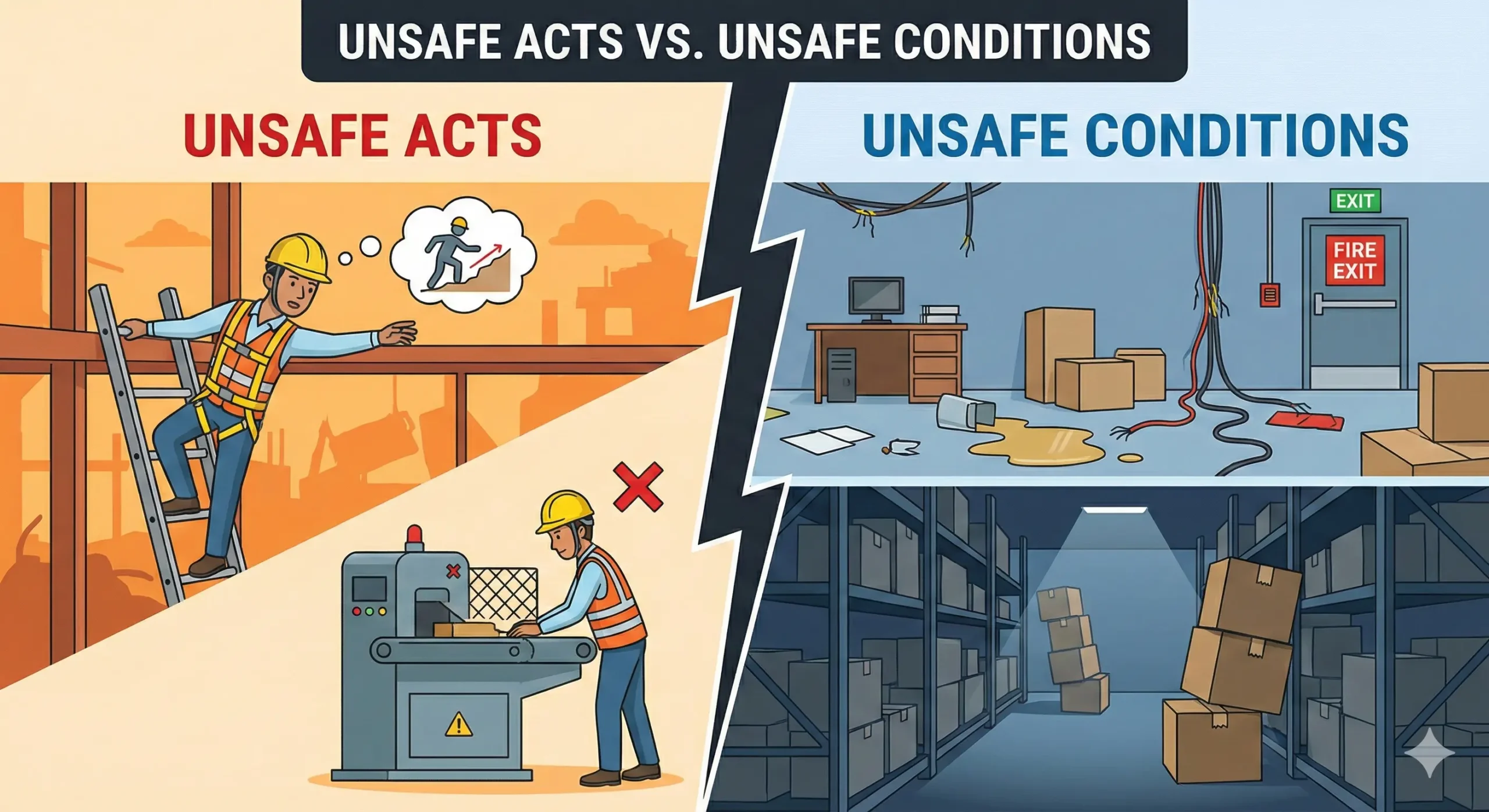
Human Error and Unsafe Acts
Many unplanned shutdowns begin with unsafe behaviors such as bypassing procedures, improper lockout practices, or incorrect equipment handling. These actions increase the likelihood of incidents that halt production.
Process Deviations and Non-Compliance
When established procedures are ignored or inconsistently followed, minor deviations can escalate into safety events requiring shutdowns for investigation or repair.
Weak Safety Culture Indicators
Plants with limited reporting, low engagement, or fear-based safety environments often miss early warning signs. These gaps allow risks to accumulate until shutdowns become unavoidable.
How Behavior-Based Safety Prevents Shutdowns
Early Risk Detection Through Observation
Behavior-based safety prevents shutdowns by identifying unsafe behaviors before they lead to incidents. Regular observations uncover trends such as repeated procedural shortcuts or inconsistent use of protective measures. Addressing these trends early reduces the likelihood of events that force operational stoppages.
Real-Time Feedback and Behavior Correction
Immediate, constructive feedback is a core BBS mechanism. When employees receive timely guidance, unsafe behaviors are corrected on the spot. This reduces error repetition and reinforces safe work practices across shifts and teams.
Reinforcement of Safe Behaviors
BBS emphasizes positive reinforcement, not punishment. Recognizing safe actions increases their frequency, which stabilizes operations and lowers incident-driven disruptions.
Alignment Between People and Processes
Shutdowns often occur when human behavior conflicts with process design. BBS aligns worker actions with operational requirements by ensuring procedures are practical, understood, and consistently applied.
Reduction of Incident Escalation
By addressing behaviors at the earliest stage, BBS limits near-misses from escalating into recordable incidents or regulatory events. This containment effect directly reduces shutdown triggers.
Key Elements of an Effective BBS Program
Structured Observation Protocols
Effective programs use standardized observation checklists focused on critical behaviors. Consistency ensures data accuracy and meaningful trend analysis.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Observation data is analyzed to identify high-risk behaviors and prioritize corrective actions. Decisions are based on patterns, not assumptions.
Leadership Participation and Visibility
When supervisors and managers actively participate, BBS becomes part of daily operations. Leadership involvement reinforces credibility and long-term adoption.
Business Impact of Behavior-Based Safety
Reduced Unplanned Downtime
By preventing behavior-driven incidents, BBS lowers the frequency of shutdowns caused by injuries, equipment damage, or investigations.
Improved Regulatory and Audit Readiness
Consistent safe behaviors support compliance with safety regulations and internal standards, reducing enforcement actions that disrupt operations.
Stronger Operational Reliability
Plants with mature BBS programs experience more predictable operations because safety risks are managed proactively rather than reactively.
Implementing Behavior-Based Safety in Industrial Plants
Baseline Behavior Assessment
Implementation begins with assessing current behaviors to establish a baseline. This clarifies which actions pose the highest operational risk.
Workforce Training and Engagement
Employees are trained on observation techniques, feedback methods, and program purpose. Engagement ensures participation is viewed as supportive, not punitive.
Ongoing Measurement and Adjustment
BBS implementation is iterative. Observation data is reviewed regularly, and program elements are adjusted to reflect changing operational conditions.
Selecting the Right Behavior-Based Safety Solution
Scalability Across Operations
The right solution supports consistent application across departments, shifts, and facilities without adding administrative burden.
Integration With Existing Safety Systems
Effective BBS tools align with current safety management systems, procedures, and reporting workflows to avoid duplication.
Actionable Insights and Reporting
Solutions should convert observation data into clear insights that guide corrective actions, training priorities, and leadership decisions.
Read More : Shutdown Safety Management Systems
Frequently Asked Questions
What is behavior-based safety in simple terms?
Behavior-based safety is a method that improves workplace safety by observing and correcting employee behaviors that influence accident risk.
How does behavior-based safety reduce plant shutdowns?
It prevents shutdowns by identifying unsafe behaviors early, correcting them before incidents occur, and reinforcing safe practices consistently.
Is behavior-based safety focused on blaming workers?
No. BBS focuses on improving systems and behaviors through positive feedback, not assigning blame.
Can behavior-based safety work alongside existing safety programs?
Yes. BBS complements existing safety management systems by addressing the human factors those systems rely on.
How long does it take to see results from a BBS program?
Results often begin with improved reporting and behavior awareness, followed by reduced incidents as the program matures.
Does behavior-based safety apply to all industrial environments?
Yes. BBS principles are adaptable across manufacturing, energy, processing, and other industrial settings.
What makes a behavior-based safety program effective long term?
Consistent leadership involvement, data-driven adjustments, and active employee participation sustain long-term effectiveness.